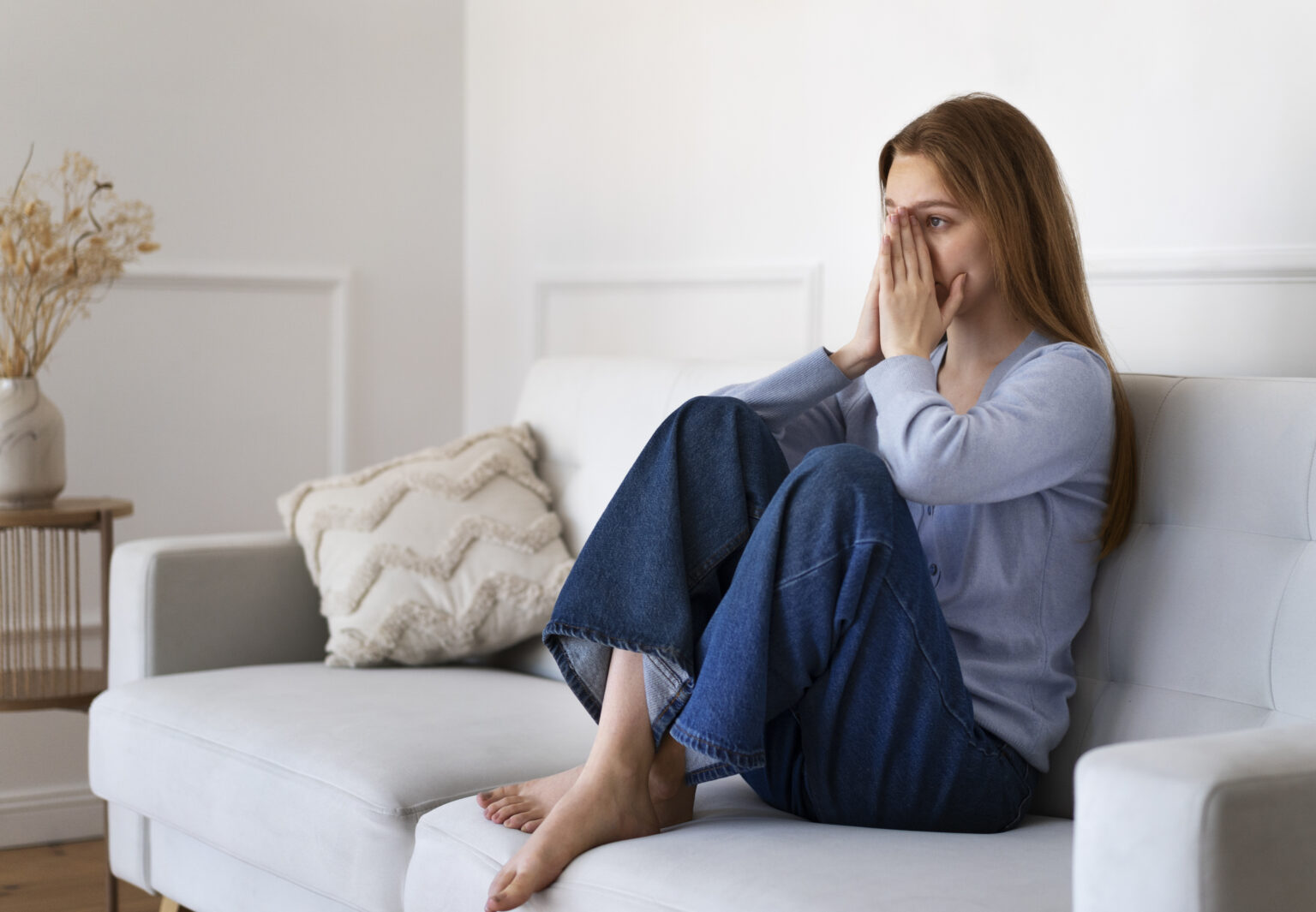
Manage and treat anxiety online
You can now connect with an online doctor for anxiety treatment online through our easy-to-use app. Propanolol is a majorly prescribed and recommended option for treating and preventing anxiety.
By getting the well-suited dose, prescription of medicines, and dosing frequency, you will get relief for all the related symptoms of anxiety. Get a prescription now with one of our doctors at Your Doctors Online.
What are the symptoms of anxiety?
If you are unsure whether you suffer from anxiety or not, here are some of the common symptoms to look for:
- Stage fright
- Fast heartbeat
- Fear of public speaking
- Getting breathless while speaking
- Restlessness and constant feelings of fear
- Shaking and trembling while speaking or doing anything in public
What are the causes of anxiety?
The causes of anxiety can stem from various factors. Some common causes of anxiety include genetics, brain chemistry, environmental stress, life experiences such as trauma or abuse, medical conditions like heart disease or thyroid disorders, drug withdrawal or misuse, and certain medications or substances like caffeine and alcohol.
Stress from major life events or accumulated everyday stressors can contribute to the development of anxiety disorders. It is important to note that anxiety disorders can be influenced by a combination of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors, making it essential to seek professional help for proper diagnosis and treatment.

What kind of treatment is there for anxiety?
The main treatments for anxiety disorders include:
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is considered one of the most effective psychotherapies for treating anxiety disorders. CBT helps patients change negative thought patterns and behaviors that contribute to anxiety.
- Applied relaxation therapy focuses on learning techniques to relax the muscles and respond to anxiety-provoking situations.
- Antidepressants like selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) are typically the first-line medication treatments for anxiety disorders.
- Other medications used include benzodiazepines, beta-blockers, anticonvulsants, and buspirone, though these are not recommended for long-term use.
- A combination of psychotherapy and medication is often the most effective approach for managing anxiety disorders.
- Regular exercise, stress management techniques like meditation, avoiding alcohol and caffeine, and getting enough sleep can also help manage anxiety symptoms.
- The search results emphasize that the specific treatment plan should be tailored to the individual based on the type of anxiety disorder, severity of symptoms, and patient preferences.
Anxiety medication we prescribe
anti depressants
Learn MoreHow to connect with doctor for Anxiety treatment
Connect with a virtual doctor and get anxiety treatment.
1
Describe your issue
Download our app, register and tell us about your medical issue to get started.
- Mental Health
- STD
- UTI
- Sexual Health
- Skin
- Allergies
2
Chat with a doctor
Connect with a board-certified doctor. You can chat, send pictures and videos.
Hi I’m Dr. Nicole. How may I help you?
Hi Dr. Nicole, I have recurrent episodes of anxiety and panic attacks. Can you help me?
3
Get online prescription
Our online doctors can help you with your medical issues and give you prescriptions.
Prescription
- Escitalopram 10mg
- Take once a day for a month
Send Prescription
How to prevent Anxiety?
To prevent anxiety, several strategies can be implemented based on the information provided in the sources:
- Staying active through regular exercise has been shown to reduce anxiety symptoms and improve overall mental well-being.
- Engaging in mindfulness practices, deep breathing exercises, meditation, and relaxation techniques can help manage stress and prevent anxiety.
- Seeking professional help, such as psychological counseling or therapy, can provide tools and strategies to prevent and manage anxiety effectively.
FAQs about Anxiety treatment online
How do anxiety medications work?
Anxiety medications work by targeting neurotransmitters in the brain, such as GABA for benzodiazepines and serotonin and norepinephrine for antidepressants, to regulate mood, reduce nerve cell activity, and create a calming effect, ultimately helping to alleviate symptoms of anxiety disorders.
How to get anxiety medication without seeing a doctor?
To get anxiety medication without seeing a doctor in person, individuals can utilize online mental health platforms that offer telehealth services like Your Doctors Online. Talk to a doctor online and get medications right away.
What is ketamine treatment for anxiety?
Ketamine is an FDA-approved medication used as an anesthetic agent during surgery. However, it is not approved for other conditions like pain, anxiety, etc. It is better to get advice from a doctor before taking any medication.
What deficiency causes anxiety and panic attacks?
If you are deficient in vitamin B6 and iron, you can experience anxiety and panic attacks. Other vitamins whose deficiency can cause anxiety include magnesium, vitamin D, selenium, antioxidants, zinc, and omega 3. Therefore, consult a doctor for your body’s health. He may recommend some tests to clearly understand what deficiencies might have caused you anxiety and panic attacks.
What is the root cause of anxiety disorder?
The root cause of the anxiety disorder is periodic stress episodes or a significant setback event that triggers excessive anxiety. In addition, some people are more prone to anxiety than others depending upon your personality type. Consult a doctor today if you experience the symptoms of anxiety.
How do I get prescribed anti-anxiety medication online?
You can get anti-anxiety medication online with Your Doctors Online. Download our app and register yourself. Describe your issue, and connect with a doctor. Get a prescription for anxiety delivered to your preferred pharmacy.
When should you get medicated for anxiety?
Anxiety medication is required if your condition is too serious to carry out day-to-day activities. Using medications can help get short-term relief and works effectively when used with therapy, exercise, and emotional support by people around you.
What happens if anxiety isn't treated?
Left untreated, it can interfere with daily activities and worsen over time. The negative consequences include loss of productivity, suicidal thoughts, disability, and risk of developing mental health issues. You can get a prescription for anxiety medications like escitalopram with our virtual telehealth services.
How long does anxiety medicine take to start working?
Anxiety medicine starts working within minutes to an hour after taking it. It helps provide quick relief to short-term anxiety and helps ease emotional as well as physical symptoms. Some prescription medications for anxiety include Citalopram (Celexa), Escitalopram (Lexapro), Fluoxetine (Prozac), Paroxetine (Paxil), and Sertraline (Zoloft).
Do anxiety meds cause weight gain?
Anxiety medications have side effects on metabolism, which can cause an increase in weight gain. Also, some people binge on food during anxiety, ultimately gaining weight.
-Phindile Mkhatshwa
-brooke snow
-Okiti Stephanie
-ASIF Khan
-Chelsey
-edith bien aime
-Lesego Thejane
-Stephanie Brown
-kulwinder gill
-Elijah Mark
Get started today
Talk to online doctors now and get medical advice, online prescriptions, refills, lab requisitions and medical notes within minutes. On-demand healthcare services at your fingertips.