Consult a fungal infection doctor online
Fungal infections can impact various body parts, including the skin, hair, nails, and lungs. Their severity ranges from mild to severe, depending on factors such as the site of infection, the type of fungus involved, and the progression of the condition.
At Your Doctors Online, our team of medical professionals is available to provide treatment and prescriptions for fungal infections. Whether you’re dealing with a mild case or a more severe condition, our doctors can offer personalized recommendations, prescribe appropriate medications, lab requisitions, and sick notes, and assist you in managing your symptoms effectively.
How to connect with doctor for fungal infections
Connect with a health care professional online in 3 easy steps.
1
Describe your Issue
Download our app, register and tell us about your medical issue to get started.
- Fungal Infections
- Anemia
- STD
- UTI
- Skin
- Covid
2
Chat with a Doctor
Connect with a board-certified doctor. You can chat, send pictures and videos.
Hey Dr. Nicole, I have a fungal nail infection. Can you help me?
3
Get Prescription
Our Online doctors can help you with your medical issues and give you prescriptions.
Prescription
- Terbinafine 1% cream
- Apply twice a day for two weeks
Send Prescription
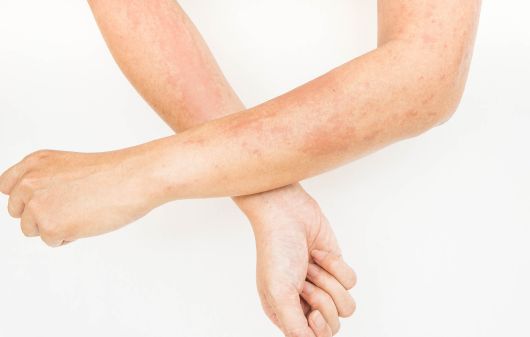
What do fungal infection look like?
Following are the symptoms of fungal infection:
- Painful or sore mouth, throat, or white patches
- Skin changes, such as cracking or peeling
- Nail discoloration, thickness, or cracking
- Cough, sometimes with blood
- Painless lump under the skin
- Muscle and joint pain
- Shortness of breath
- Abdominal pain
- Light sensitivity
- Blurred vision
- Night sweats
- Headache
- Nausea
- Fatigue
- Itching
- Fever
What causes fungal infections?
Fungal infections arise from yeast, molds, and other fungal types. Although most fungi are harmless, a few can lead to diseases, particularly in opportunistic situations such as weakened immune systems. Common fungi causing infections include:
- Dermatophytes: These fungi rely on keratin found in hair, nails, and outer skin layers, causing no harm to living tissue.
- Candida: Candida albicans, a usually benign yeast residing on the body, can overgrow, resulting in itching and redness and rarely leading to severe infections.
- Environmental fungi from soil or water, like Histoplasma, coccidioides, Blastomyces, and Aspergillus, can also cause infections.

Fungal infection medications we prescribe online
Antifungal
Learn MoreAntifungal
Learn MoreAnti Protozoals
Learn MoreAntifungal
Learn MoreAntifungal
Learn MoreHow to treat fungal infections?
When it comes to treating fungal infections, various types of antifungal medications are available online. These medications work by targeting different aspects of fungal cell structure and function. Here are the three main types of antifungal medications and examples of each:
Azoles
Azoles are commonly used to treat skin and mucous membrane infections. They interfere with an enzyme crucial for fungal cell membrane synthesis, leading to cell instability and eventual death. Examples of azoles include:
- Ketoconazole
- Clotrimazole
- Terconazole
- Fluconazole
- Itraconazole
Polyenes
Polyenes work by increasing the porosity of the fungal cell wall, ultimately causing the cell to become compromised and prone to bursting. They are often used to treat Candida yeast infections, including mucosal or invasive Candida infections. Examples of polyenes include:
- Amphotericin B
- Nystatin
FAQs about fungal infection treatment
How do doctors treat fungal infections?
Doctors commonly prescribe standard medications to treat fungal infections. Additionally, they may recommend other drugs, such as boric acid, nystatin, or flucytosine. Oral yeast infection treatments may include clotrimazole, fluconazole, miconazole, or nystatin. Treatment options for ringworm of the skin may also be prescribed.
How do you completely cure a fungal infection?
Treatment for skin fungus typically involves using antifungal creams, many of which are available over-the-counter. In severe cases, stronger prescription medications or oral antifungal medicines may be necessary for faster and more effective treatment.
Do I need to see a doctor for fungal infection?
Fungal infections can be contagious and may spread from person to person or from infected animals, soil, or surfaces. If you experience signs or symptoms of a fungal infection, it's advisable to schedule an appointment with your doctor for evaluation and appropriate treatment.
How do you stop a fungal skin infection from spreading?
To prevent the spread of a fungal skin infection, keep the affected skin areas clean and avoid sharing towels, bath mats, or other personal items with others. Additionally, wash your hands thoroughly after treating the infection to minimize the risk of spreading it to other parts of your body or to other people.
What are the best treatments for face fungal infections?
For facial fungal infections, most providers prescribe topical ointments and creams. A doctor may recommend antifungals with higher potency if the infection is severe. Consult our doctors at Your Doctors Online for the treatment and prescription of facial antifungals.
Are there over-the-counter treatments available for fungal skin infections?
Over-the-counter antifungal creams are commonly used to treat mild and common fungal skin infections such as ringworm, jock itch, and athlete's foot. Some of these creams are also suitable for treating vaginal yeast infections. However, in certain cases, prescription antifungal creams may be stronger or more effective for specific types of fungal infections.
Is it necessary to consult a doctor for the treatment of fungal infections?
Over-the-counter antifungals can help for mild infections, but for severe infections, you need more potent antifungals available on prescription only. You can consult a doctor at Your Doctors Online for the prescription of appropriate antifungals for your condition.
What is the standard duration of treatment for fungal infections?
To treat fungal infections, a window of two weeks is a standard duration. However, it takes 4-6 weeks to recover from the skin and hair infection.
-Phindile Mkhatshwa
-brooke snow
-Okiti Stephanie
-ASIF Khan
-Chelsey
-edith bien aime
-Lesego Thejane
-Stephanie Brown
-kulwinder gill
-Elijah Mark
Get Started Today
Talk to online doctors now and get medical advice, online prescriptions, refills, lab requisitions and medical notes within minutes. On-demand healthcare services at your fingertips.