Overview
Your acne products could be causing your pimples! Check out our guide to pityrosporum folliculitis. The little red bumps actually get worse when using acne treatments.
Are you wishing for clear skin, but everything you try seems to be making it worse? Your issue may not even be acne, but folliculitis. A skin condition that closely resembles acne can even lead doctors to misdiagnose it, and using acne products for it can actually exacerbate the condition. We asked one of our resident GPs, Dr. Honaker, to lend us his insights on this common skin condition.
What Is Pityrosporum Folliculitis (Malassezia)?
This common skin condition often mimics acne, which occurs when yeast bacteria, which naturally occur on the skin, invade the skin and enter the hair follicles. Once it gets into the hair follicles, it will multiply and cause itchy, acne-like bumps on the skin.
How is it Different from Other Types of Folliculitis?
Many forms of folliculitis (think razor burn, hot tub folliculitis, and barber’s itch) are caused when bacteria, fungi, or a virus can penetrate damaged hair follicles. The hair follicles are damaged by everyday activities such as:
- Rubbing or scratching your head
- Habitual wearing of hats or helmets
- Improper shaving methods
- Wearing tight clothing
- Allowing hair products to build up on the scalp
- Visiting hot tubs, whirlpools, or heated pools that are not properly maintained
Pityrosporum folliculitis differs from other types of folliculitis because an overgrowth of yeast causes it.
The yeast that causes pityrosporum folliculitis is different from the yeast that causes yeast infections (thrush) or the yeast used in baking. This yeast is naturally occurring on the skin and usually does not cause any issues.
Another difference is that many forms of folliculitis can clear up without medical intervention, and applying an antibiotic cream or antibacterial soap can aid the healing process.
A study determined that pityrosporum folliculitis was more common after antibiotic use. Unlike most types of folliculitis, pityrosporum folliculitis improved after oral or topical antifungal use.
Signs and Symptoms of Pityrosporum Folliculitis
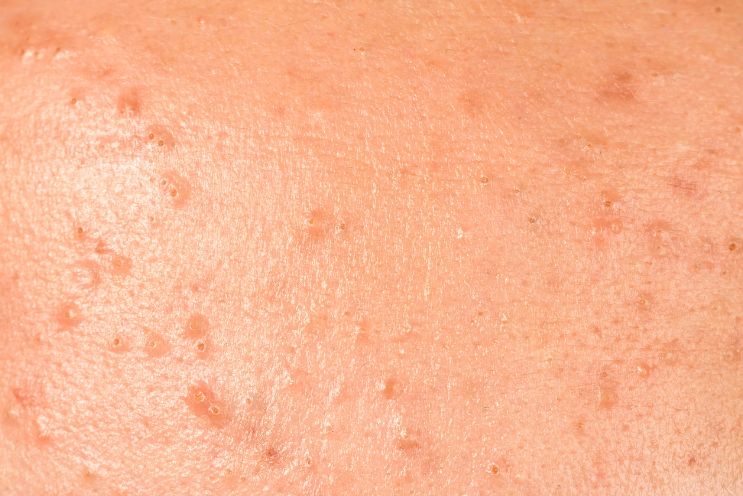
This type of folliculitis can leave bumps that are 1-2 mm in diameter and may or may not contain pus. The bumps are approximately the size of a pin and uniform in appearance. It is common to find these bumps on the upper chest and upper back. Some patients will be affected on their forearms, face, and lower legs.
While often mistaken for acne, it is possible to have both conditions simultaneously, as many people with oily skin are affected by both.
Many patients seek out treatment for this type of folliculitis because it can be very itchy. The itchiness can come on sporadically and be followed by a stinging sensation. After scratching, you may notice a red hive-like appearance on the skin.
Risk Factors for Pityrosporum Folliculitis
The condition can affect young to middle-aged adults of either sex. It is often associated with those who suffer from seborrheic dermatitis or severe dandruff.
While the exact reasons for the development of pityrosporum folliculitis is not known, it is believed that external factors or a weakened host may play a factor.
The following are also believed to be associated with the development of pityrosporum folliculitis:
- Wearing synthetic fabrics that don’t allow the skin to breathe can be associated with pityrosporum folliculitis, as yeast can grow in warm, moist, and sweaty environments.
- Using greasy sunscreens and oily moisturizers
- Suppose you have naturally oily skin. Yeast feeds on skin oil. The production of skin oil largely depends on your hormone levels.
- A decreased resistance to microorganisms
- Oral steroids such as prednisone
- Diabetes
- Oral contraception pill
- Being overweight, which can result in tight clothes and excessive sweating
- Stress or fatigue
What is the difference between Pityrosporum folliculitis and acne?
Pityrosporum folliculitis is often misdiagnosed as acne because the differences between the two conditions are relatively mild.
Unfortunately, acne treatment can actually contribute to the development of pityrosporum folliculitis. This is because yeast and bacteria are naturally in competition on the skin. When medication is taken for acne, the bacteria are diminished, allowing the yeast to overgrow.
How is Pityrosporum Folliculitis Diagnosed?
Obtaining a proper diagnosis can be challenging, as this skin condition closely mimics acne. If you are getting acne treatment and it is not improving, asking your dermatologist to screen you for folliculitis can be a good step.
Screening for Folliculitis
Getting screened for folliculitis is a simple procedure done by a dermatologist. The affected area will be gently scratched to obtain a cell sample. The sample will then be examined under a microscope to evaluate and test for folliculitis.
How do you get rid of Pityrosporum folliculitis?
Some factors can make this type of folliculitis difficult to treat. To prevent the condition from returning, the yeast overgrowth and the predisposing factors that contributed to it must be addressed. Unfortunately, these reasons are not always clear. In these cases, the folliculitis will reappear once the anti-yeast treatment is stopped.
To fully eradicate folliculitis, you must address the reason for its original cause. This may mean
- Losing weight
- Discontinuing your acne treatment
- Wearing more breathable fabrics
- Changing the type of moisturizer or sunscreen used
- Changing the type of contraception used
- Practicing more self-care
Types of Treatment for Pityrosporum Folliculitis
Topical treatments
Topical therapy is not always effective, but it is a good first step to eradicating folliculitis. These treatments can include:
- Nizoral or Selsun Shampoo-apply weekly for 10 minutes in the shower and then rinse
- Apply 50% propylene glycol in water with a gauze pad, applying it twice daily for three weeks, then reduce to twice a week for maintenance.
- Spray Lamisil solution on the affected area daily for 14 days, and then weekly treatments
- Loprox or Nizoral can be used for spot treatments
Oral Treatments
Oral treatments are considered to be the most effective for this type of folliculitis. These treatments include:
- Nizorol
- Sporonox
- Accutane
Most treatments take between 7 and 14 days to see a difference, and recurrences are expected.
Home Remedies
There are some easy ways to treat your pityrosporum folliculitis at home. Here is a list of some home remedies to tame the yeast growth.
- If your symptoms are occurring around your hairline, a selenium sulfide shampoo, such as Head & Shoulders or Neutrogena, may help.
- Apply diluted tea tree oil to the area with a cotton pad twice daily
- Bathe in a sea salt bath to help dry out the infection
How to Prevent Pityrosporum Folliculitis
This type of folliculitis can be challenging to prevent, but there are still steps you can take to protect your skin from yeast overgrowth.
- Wash with antifungal shampoo and soap to discourage yeast overgrowth
- Use a gentle oil-based astringent daily on the areas of your skin that are especially oily
Instead of spending your time guessing what your skin condition is, why not connect with a real doctor who can put your mind at ease within minutes?
FAQs About Pityrosporum Folliculitis Answered by Your Doctors Online Team
Your doctor will treat pityrosporum folliculitis with antifungals as needed, based on your condition. They may start treatment with an antifungal cream or, in case of severe infection. Additionally, they may prescribe antifungal medications.
Commonly affected body parts include:
Face/forehead
Scalp.
Shoulders.
Arms.
Back.
Chest.
Pityrosporum folliculitis may be contagious as it can be spread through hot tubs, shared razors, or, rarely, through skin-to-skin contact between people.
Antifungal pills may cause side effects such as nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, or diarrhea.