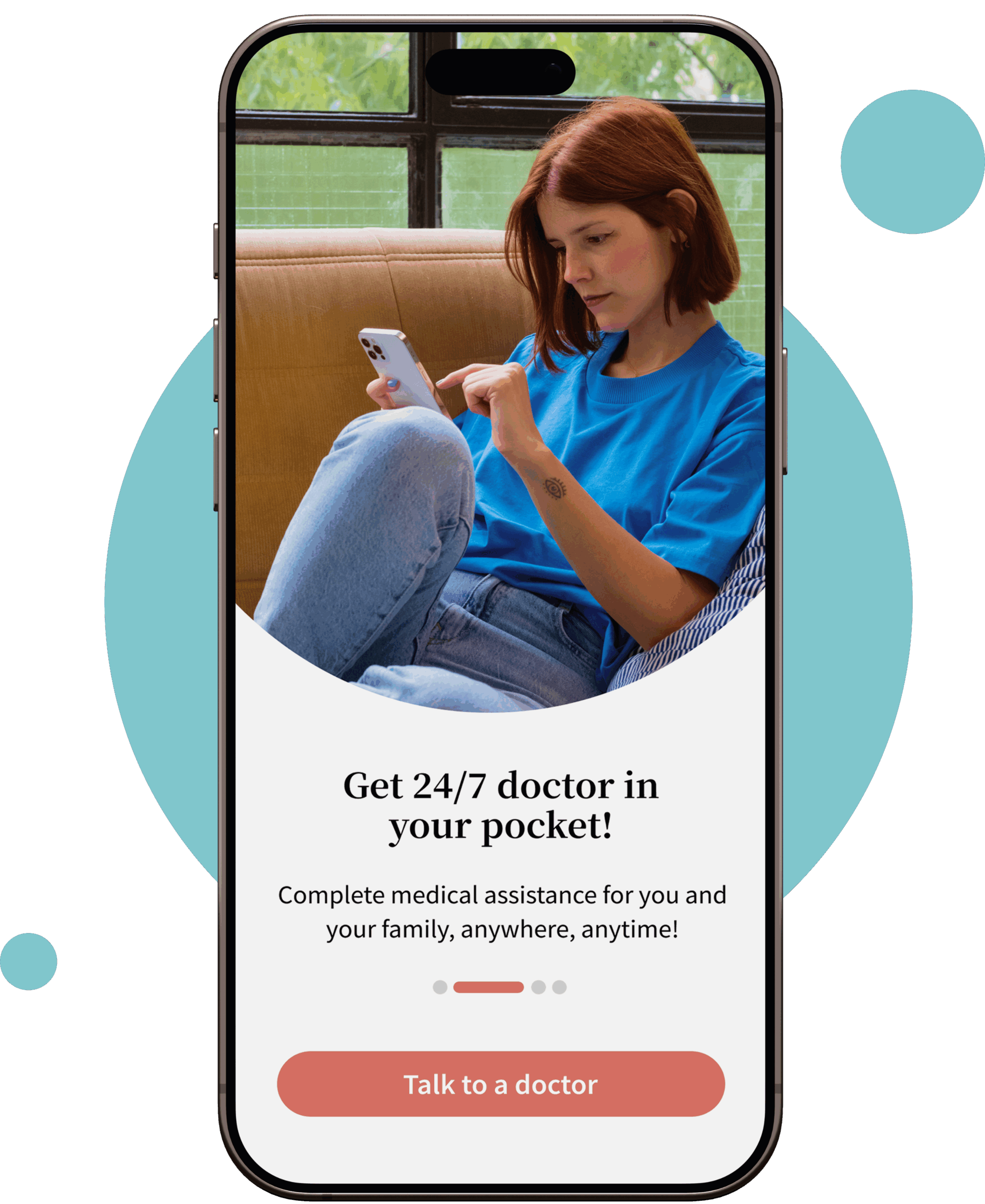
Get the prescription for Imodium online
Imodium (loperamide) is an antidiarrheal medication used to treat diarrhea, anal leakage, and loose motions.
Getting an Itraconazole (loperamide) prescription from us is straightforward and effortless; you can connect with a qualified doctor anytime through “Your Doctors Online” to discuss your presenting symptoms. However, an Imodium prescription will only be provided after consultation with our qualified doctor and if the treatment is completely safe for your unique needs.
How to get prescription online?
Get online prescription in three easy steps
1
Describe your issue
Download our app, register and tell us about your medical issue to get started.
- Gastro
- Anemia
- STD
- UTI
- Skin
- Covid
2
Chat with a doctor
Connect with a board-certified doctor. You can chat, send pictures and videos.
Hi Dr. Nicole; I am on chemotherapy and have had frequent diarrhea for the past two days. It’s been tough to manage. Can I get some form of treatment, please?
3
Get prescription
Our online doctors can help you with your medical issues and give you prescriptions.
Prescription
- Loperamide, 4 mg starting dose,
- Followed by 2 mg every two hours; maximum daily dose 16 mg.
Send Prescription
What is Imodium?
Imodium (Loperamide) is an FDA-approved antidiarrheal medication prescribed to treat diarrhea/loose motion or watery stools.
Imodium (Loperamide) medication, either prescription or over the counter, should be taken with caution as it rarely can initiate abdominal cramps. Use under two years is discouraged by the Food and Drug Administration. Caution is advised due to possible drowsiness, and alcohol and caffeinated foods should be avoided.
Important Information About Imodium
Following are some points that you should know about Imodium:
Common side effects: are constipation, abdominal discomfort, and nausea.
Serious side effects: include allergic reactions and severe or persistent constipation.
FAQs About Imodium
How does Imodium work?
Imodium works by slowing down the gastrointestinal movement that delays the reabsorption of meals. This results in more absorption of water and low stool output, which increases the diarrhea and recovers water loss from the body to a greater extent.
How to take Imodium?
Immodium is usually recommended and prescribed right after passing the loose or watery stool. It can be taken in the form of Pills (tablets) and liquid form, as both are considered to provide instant relief from diarrhea.
What not to take with Imodium?
Medications like clarithromycin, omeprazole, and some antidepressants like fluoxetine and citalopram will interact with Imodium. It is better to consult the healthcare provider before taking Imodium to avoid any unwanted effects.
How quickly does Imodium work?
Loperamide will start to act 30 minutes after being taken orally and is considered the quickest to work for the loose stool. Immodium will more likely treat your diarrhea in 2 days completely.
Is liquid Imodium better than pills?
Both are used to treat diarrhea. Liquid imodium is better in absorption as it is already in liquid form and absorbs more quickly than tablets in compact form.
How much Imodium to take for diarrhea?
Taking (2 tablets of 4mg) is usually prescribed right after the loose stool. Imodium daily dose depends on age or weight: adults start with 4 mg and take 2 mg per loose stool (up to 16 mg/day).
Can I take pepto bismol and Imodium together?
One or more medications may become less effective due to interactions. They may also make you more susceptible to negative consequences. Imodium A-D and Pepto-Bismol shouldn't be taken concurrently because of this. Combining them will make them less effective for you.
How many days can you take Imodium?
Loperamide is often only required for 1 to 2 days per person. If you have diarrhea due to a bowel disorder such as Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, or short bowel syndrome, you may need to take it more extended.
What are the alternatives to Imodium?
Lomotil, Pepto-Bismol, and Kaopectate are a few further popular medications for treating diarrhea.
What happens if you take Imodium on a full stomach?
Taking Imodium on a full stomach may delay its absorption and onset of action. Taking Imodium before or after a meal is generally recommended for optimal effectiveness.
Can I take Imodium and drink alcohol?
You run a higher risk of Imodium overdose if you combine it with alcohol. Alcohol can irritate the GI tract but won't prevent the loperamide from working. It can appear that the loperamide isn't working because that can make diarrhea problems worse.
Does Imodium help with gas and bloating?
Simethicone, a component of IMODIUM, eases excess gas in the intestines and relieves bloating and pain brought on by gas.
What happens if you take too much Imodium?
You won't likely be hurt if you take one extra dose of loperamide. Higher dosages, however, can result in life-threatening heart issues. The symptoms include a rapid or erratic heartbeat.
-Phindile Mkhatshwa
-brooke snow
-Okiti Stephanie
-ASIF Khan
-Chelsey
-edith bien aime
-Lesego Thejane
-Stephanie Brown
-kulwinder gill
-Elijah Mark
Get started today
Talk to online doctors now and get medical advice, online prescriptions, and referrals within minutes. On-demand healthcare services at your fingertips.