Get Cellulitis treatment online
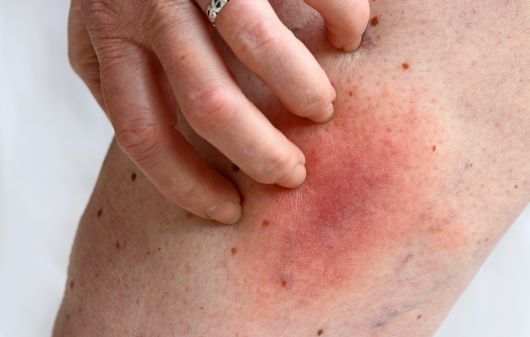
Cellulitis is a skin infection that causes swelling and painful blisters on the legs, arms, and other body parts. It is a bacterial infection that goes away within 3-5 days with antibiotic treatment.
Get a consultation from our doctors for the prescription of cellulitis online. You can get a prescription delivered to your preferred pharmacy in less than an hour.
How to connect with doctor for Cellulitis
Connect with a health care professional online in 3 easy steps.
1
Describe your issue
Download our app, register and tell us about your medical issue to get started.
- Skin
- Sexual Health
- Anemia
- STD
- UTI
- Covid
2
Chat with a doctor
Connect with a board-certified doctor. You can chat, send pictures and videos.
Hi Dr. Nicole, I have painful blisters with swelling and redness on my lower leg. Could this be due to Cellulitis?
3
Get online prescription
Our Online doctors can help you with your medical issues and give you prescriptions.
Prescription
- Cephalexin 500mg
- Take four times a day for seven days
Send Prescription
How do I know I have Cellulitis?
The symptoms of cellulitis are as follows:
- Affects one side of the body
- Painful blisters
- Skin dimpling
- Tenderness
- Redness
- Swelling
- Fever
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) worsens cellulitis as it cannot be treated with common antibiotics.

FAQs about Cellulitis treatment online
What is Cellulitis?
Cellulitis is a skin infection caused by bacteria causing swelling, pain, and redness in the affected area. The infection causes blisters and swelling on the legs, arms, and other body parts. It can also spread to other body parts if not treated promptly.
What is the fastest way to get rid of Cellulitis?
The fastest way to get rid of cellulitis is an oral antibiotic per your doctor’s prescription. It will take at least three days to reduce the symptoms and for the infection to heal, while the bacteria will be removed from the body once you complete the antibiotic course, i.e., in 5-10 days.
How to treat Cellulitis on legs?
To treat cellulitis on the legs, your doctor will recommend an antibiotic course to kill the bacterial infection. Keep your legs elevated to speed up healing, decreasing inflammation and swelling and speeding up recovery.
What are the Cellulitis healing stages?
When the cellulitis starts healing, you will notice reduced swelling, less redness and firmness around the affected area, less pain, and a lightening of the rash. The infection may appear worse during the first two days due to inflammation. Wait at least 48 hours for signs of improvement. After three days, pain decreases, swelling reduces, and warmth in the infected area lessens. After five days, the affected skin becomes less tender after a noticeable decrease in pain, swelling, and redness. Finally, after ten days, most or all symptoms should subside if the body responds well to antibiotics. A 10-day course is usually prescribed, but a five-day period can also be practical.
What is the treatment for periorbital Cellulitis?
Periorbital cellulitis is an eyelid infection, and the best treatment for cellulitis is an antibiotic medication that targets the infection-causing bacteria, i.e., streptococcus species.
How Is Cellulitis Treated When MRSA Causes it?
Cellulitis can be treated with an oral antibiotic, and the symptoms improve within three days. However, the course is completed in 5-10 days. If MRSA causes cellulitis, the treatment includes Cephalexin (500mg) four times a day and Trimethoprim-Sulfamethoxazole (800mg/160mg) for five days, taken twice daily.
What is the strongest medicine for Cellulitis?
The strongest medicines for cellulitis include antibiotics like Cephalexin, Trimethoprim, Doxycycline, Clindamycin, and Sulfamethoxazole.
Can online doctors treat Cellulitis?
Yes, online doctors can treat cellulitis and its associated symptoms without waiting in a queue for hours. At Your Doctors Online, you can get cellulitis treatment from professional doctors and get your prescription delivered to your local pharmacy.
Is bed rest good for Cellulitis?
Yes, plenty of rest helps speed recovery, reducing swelling and pain. Some over-the-counter medicines like ibuprofen and acetaminophen can also help reduce the pain.
How can I prevent Cellulitis from getting worse?
The best way to control the infection is to use an antibiotic course prescribed by your doctor. However, certain practices can help contain the infection and stop making it worse, like quick wound treatment, fulfilling the moisture requirement of the skin, and keeping the skin clean. Moreover, avoid any physical injuries or nail scratches. If you have any accompanying medical issues, get their treatment alongside them.
Is there any over-the-counter medicine for Cellulitis?
Some over-the-counter medicines for cellulitis include nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like acetaminophen and ibuprofen, which ease inflammation and reduce pain and swelling in the affected area. These medicines can only improve the symptoms, but you need prescription antibiotics to kill the bacteria and treat the infection.
What triggers Cellulitis?
Cellulitis is caused by bacteria usually present on the skin. When this bacteria enters the body through the damaged skin, it causes infection. Get personalized treatment for cellulitis with Your Doctors Online within minutes.
What are the signs that Cellulitis is getting worse?
If you experience symptoms like pain, swelling, redness, and pus, consult a doctor as the infection progresses. If left untreated, it can spread to other body parts as well.
How long does it take Cellulitis to go away with antibiotics?
Completing your antibiotic course for cellulitis prescribed by your provider is important. It usually takes 7-10 days for the infection to go away fully.
-Phindile Mkhatshwa
-brooke snow
-Okiti Stephanie
-ASIF Khan
-Chelsey
-edith bien aime
-Lesego Thejane
-Stephanie Brown
-kulwinder gill
-Elijah Mark
Get started today
Talk to online doctors now and get medical advice, online prescriptions, refills, lab requisitions and medical notes within minutes. On-demand healthcare services at your fingertips.